UK interest rates cut for first time in over four years

 PA Media
PA MediaInterest rates have been cut for the first time in more than four years, but the Bank of England has warned that borrowing costs will not fall sharply in the coming months.
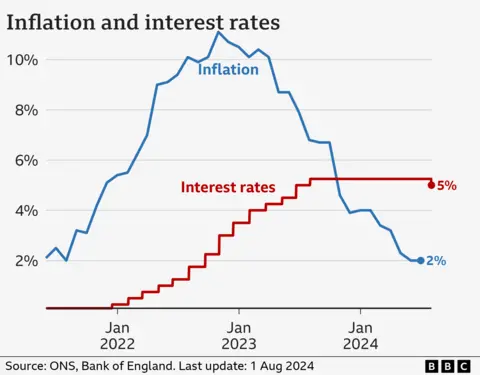
In a closely-run decision, rates were lowered to 5% from 5.25% on Thursday, marking the first cut since the onset of the pandemic in March 2020.
Interest rates dictate the cost of borrowing set by High Street banks and money lenders for the likes of mortgages and credit cards.
Andrew Bailey, governor of the Bank of England, said while policymakers voted in favour of a cut, they needed make sure that inflation, the pace of prices rises, remained low.
Interest rates have climbed over the last few years, putting pressure on household finances, although returns on savings have improved.
The fall to 5% means that some homeowners not on fixed-rate deals will see an immediate drop in their monthly mortgage payments but savers face getting a lower rate of return.
Commenting on the decision to lower rates, Mr Bailey said: “Inflationary pressures have eased enough that we’ve been able to cut interest rates today.”
But he struck a note of caution against expectations there would be a rapid fall in borrowing costs.
“We need to make sure inflation stays low and be careful not to cut interest rates too quickly or by too much,” he said.
Mr Bailey was later asked by reporters if the interest rate cut was “one and done” – that is – will there be no more cuts after this?
He responded by saying he has no view on path of rates and the Bank will decide from meeting to meeting.
The decision by the Bank’s nine-member committee was finely balanced – five, including governor Andrew Bailey, voted for a quarter point cut.
The Bank’s chief economist Huw Pill was in the minority of four who voted to hold interest rates.
 Tommy Lumby / BBC
Tommy Lumby / BBCThe interest rate cut will be a boost for some homeowners. But the Bank of England signalled that a mortgage shock still lay ahead for others.
Around a third of people with a fixed-rate mortgage are still paying less than 3%, after getting a deal when interest rates were a great deal lower.
The Bank said that most of these home loans expire before the end of 2026 “meaning that effective interest rates will rise somewhat further over that period”.
The inflation rate – which measures the pace of price rises for goods and services – hit the Bank’s 2% target in May and remained there in June.
However core inflation, which strips out volatile elements such as food and fuel prices, remains comparatively high. And the Bank expects inflation to rise in the second half of this year as energy costs tick higher in the colder months.
The Bank noted that wage growth – which can worsen inflation – had slowed but committee members continued to monitor it.
The Bank does not, however, expect a recent public sector pay rise promised by Chancellor Rachel Reeves to have a major impact on inflation.
Ms Reeves said the cut was “welcome”, but added “millions of families” were still facing higher mortgage rates, which she said was due to former Prime Minister Liz Truss’s mini-budget.
She added that the government was “taking the difficult decisions now to fix the foundations of our economy after years of low growth”, which would “make every part of our country better off”.
Growth forecast upgraded
Ms Reeves confirmed offers of wage increases of between 5% and 6% for public sector staff including NHS workers and teachers on Monday.
She also claimed the Conservative government had left a £22bn “black hole” in public finances and attempted to cover it up.
The Tories have refuted this, claiming that Labour is laying the groundwork for tax rises at the Budget on 30 October.
The Bank confirmed that it had been briefed by the Treasury about the figures on Monday before Ms Reeves made her statement in the House of Commons.
It said that it was too late to include any effect from Ms Reeves’ announcement on Monday – when she also scrapped a number of public spending projects – in its Monetary Policy Report.
Otherwise known as the Bank’s inflation report, it sets out growth forecasts for the UK economy and is published four times a year.
The Bank upgraded its outlook for the UK’s economic growth between April and June this year. It now expects gross domestic product to expand by 0.7%, up from a previous forecast of 0.2%.
But growth is expected to slow in the second half as businesses reported weaker momentum.
Source link